Abstract
Introduction: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is standard therapy for selected patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM). Studies in MM and lymphoma have suggested that ability to mobilize and collect a higher yield of CD34 + cells predicts for improved survival outcomes, perhaps reflecting better bone marrow reserve (Bolwell 2007, Raschle 2011). We aimed to validate this hypothesis by correlating high CD34 + cell collection ("supermobilizers") and survival outcomes in a large myeloma cohort with long follow-up.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed MM patients (pts) who underwent ASCT at our centre 2000-2010, correlating number of CD34 + cells collected with post-transplant progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Stem cells were mobilized using cyclophosphamide 2.5 g/m 2 IV (day 1), G-CSF 10 ug/kg/day SC (starting on day 4), and leukapheresis (day 11), targeting 4x10 6/kg but accepting a minimum of 2x10 6/kg to support a single transplant. Using a cut-off used in previous studies, pts were categorized as "supermobilizers" if ≥8x10 6/kg CD34+ cells were collected.
Results: 621 pts were analyzed. Most pts (422/605; 70%) received high dose dexamethasone (HDD) alone or in combination with vincristine and adriamycin (VAD) for pre-transplant induction therapy (pre-dating the novel agent era) with only 18% (110/605) receiving more contemporary bortezomib-based induction (mostly cyclophosphamide, bortezomib and dexamethasone; CyBORD). The median number of CD34 + cells collected for all pts was 13.9x10 6/kg (range 2.1-61.8). The median CD34 + cells re-infused was 6.2x10 6/kg (range 2.1-25), as some cells were reserved for 2 nd ASCT, but median CD34+ cells collected correlated with CD34 + cells infused (Pearson coefficient 0.81, p<0.001).
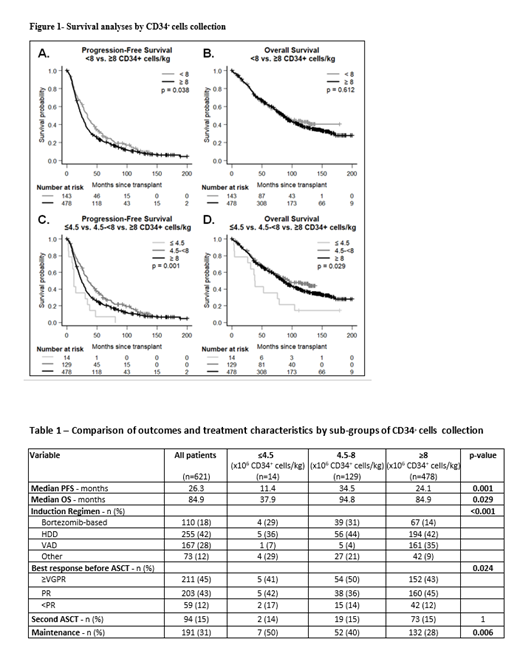
At a median follow-up of 74 months (m), we were surprised to report an inferior PFS of 24.1m for the supermobilizers collecting ≥8x10 6/kg vs 33.7m for the <8 group (p=0.038, Figure 1a), without differences in OS (p=0.612, Figure 1b). No further discrimination in PFS was observed when using a more extreme supermobilizer cut-off of 15x10 6/kg. To further understand the counterintuitive result of shorter PFS with higher mobilization capacity, we explored the continuous relationship between CD34 + cells and PFS, identifying another optimal cut-off of 4.5x10 6/kg. Pts collecting in the mid-range (4.5-8; n=129) achieved the best PFS of 34.5m, significantly improved over 24.1m in the ≥8 group (n=478) and 11.4m in the small group at the extreme lower collection range (n=14; ≤4.5x10 6/kg)(Figure 1c). A similar pattern was seen with OS (Figure 1d). Clinical and laboratory parameters that may impact both collection capacity and survival, such as age, ISS, and kidney dysfunction, were investigated as confounders but were similar between collection groups and did not predict for PFS in multivariable analyses. Treatment variables, however, differed between groups: the lower collection groups more often received bortezomib-based induction (29%, 31% and 14% in the ≤4.5, 4.5-8 and ≥8 groups, respectively, p<0.001) resulting in deeper responses pre-transplant (VGPR 50% in the ≥8 group vs 43% in the 4.5-8 group, p=0.024) (Table 1). Use of maintenance therapy post-ASCT also differed (50%, 40% and 28% in the ≤4.5, 4.5-8 and ≥8 groups, respectively, p=0.006).
Discussion: In this large cohort of 621 MM patients, we report that "supermobilizers" who collected ≥8 x 10 6 CD34 + cells/kg exhibit inferior PFS from transplant than those with less robust mobilization. We suspected that this unexpected observation was due to confounding variables, and identified differences in treatment, primarily greater use of bortezomib-based induction and post-transplant maintenance therapy in the lower collection group. This group was able to achieve deeper responses (≥VGPR) even before transplant than the supermobilizer group, leading to improved PFS. Although bortezomib is routinely used as induction therapy pre-transplant currently and is not felt to be stem cell toxic, it may impair mobilization to a lesser degree, leading not to abject failure of collection but lowered capacity to achieve "supermobilizer" status. Although more research is needed to validate this hypothesis, we can at minimum conclude that high stem cell collection does not appear to predict for a long-term survival advantage.
Reece: Millennium: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding. Trudel: Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy. Prica: Astra-Zeneca: Honoraria; Kite Gilead: Honoraria. Chen: Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astrazeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy.